In an age of increasing sophistication of cyber attacks, governments and partner organisations often find themselves as a target. These attacks often focus on identity, which can cause damage in the form of unencrypted data. Should hackers be successful in their attempts, it is possible they could allow fraudsters to manipulate electronic data in secure documents to illegally pass border crossings and inspection points and facilitate identity theft to access confidential data in government eServices, seriously undermining national security and the trust in digital transactions.
This blog will look at the efforts being made to secure these digital transactions, and why cyber security resilience needs to be front and centre.
Embedded software solutions
Embedded software solutions have played a key role in protection against cyber attacks. These solutions securely combine dedicated security IC hardware with chip operating system and software applications. Biometric passports and electronic ID cards embed such chip and software solutions to securely store sensitive data and cryptographic keys and to safely execute cryptographic procedures to assure authenticity and encryption of all communications.
As one of the smallest instances of advanced IT solutions available in the industry, secure embedded software in electronic documents, and their cyber security status, are the object of deep care and attention – and are at the center of rigorous Common Criteria (CC) security evaluations.
Changes in legislation
The Cybersecurity Act came into force in June 2019. The act established an EU framework for cybersecurity certification to ensure a common approach in the European internal market.
One of the key takeaways focuses on how to assure that a product can be operated securely long-term over its intended productive life, even despite adverse cyber events.
The security of an ID product and its strength to resist latest emerging cyber threats now must be assessed at least every 5 years to withhold valid CC certification. The ability to update the product with a patch, both for new and already issued documents, is highly recommended in anticipation to cyber threats.
Achieving cyber resilience in ID issuance solutions
At Thales, our approach is fully in line with the recent changes to CC evaluation and certification scheme. The latest versions of our embedded SW products have undergone recent CC security evaluation and certification at the highest possible level. This will be monitored closely to anticipate any potential vulnerability. We can implement Operating System (OS) agility with the ability to patch remotely in real-time.
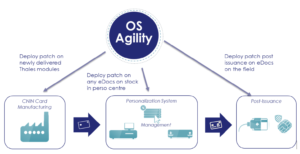
The ability to update embedded software products, i.e. patched even on the field, is a key element to achieve cyber resilience – with our solutions designed to take information security, business continuity and organizational resilience into account. It involves issuance and post-issuance solutions to convey a security update to all concerned documents, and additional solutions and services to protect these IT solutions from cyber threats themselves.
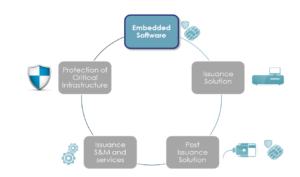
This Post-Issuance solution with new patch management capabilities is key for cyber resilience in the field to ensure that electronic documents can be securely used over the full length of the operational lifetime. The solution is user-centric and web-based to manage ID document security, usage and scalability – and can carry out the following:
- Installing and upgrading applications
- Card activation / unblocking
- PIN management
- Loading & renewing certificates
- Data and card profile updates
- Applying OS security upgrades
- Post-issuance OS upgrade via Thales Digital ID companion
OS security upgrades can be deployed using various channels; inspection terminals, kiosks, self-service government portals and mobile. The authenticity and approval of any patch is assured by digital signature by both Thales and the document issuer and patch data is always encrypted. Only the documents explicitly target to be updated can decrypt, verify and install an OS patch. No user or confidential data is read or temporary backed-up during the upgrade operation.
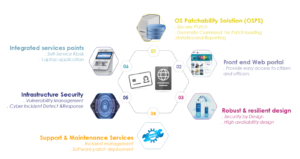
To provide highest protection against any cyberattack on the issuance or post-issuance infrastructure itself, Thales can provide a whole range of additional cyber resilience systems and services, from software support and maintenance to vulnerability management and dedicated incident detection and response solutions.
For further reading: