Connectivity is on the rise globally with more than 2.3 billion connected consumer devices such as smartphones, wearables, laptops and tablets expected to be shipped by 2025. As for IoT devices, it is expected that more than 3 billion devices will be connected to cellular networks over the next five years and eSIM capable devices will exhibit CAGR of 40%.
To keep up with this tremendous growth there is a need for ensuring secure and seamless cellular connectivity. With devices needing SIMs to authenticate them for mobile networks, advances in SIM technology will be critical for the expansion of the connected world in years to come.
So how can manufacturers seamlessly manage this growth, while also ensuring secure access to cellular networks? The solution lies in a new eSIM form factor, also known as integrated SIM (or iSIM).
The integrated SIM (iSIM) provides a secure way of authenticating devices with the same security and convenience as the eSIM. iSIMs are embedded within a trusted, tamper-resistant enclave into a device’s System on Chip (SoC) and contain a secure vault for storing mobile subscription details. This simplifies the adoption of eSIM technology while also optimising costs and performance. The integrated SIM mirrors the specification and certification of the integrated eUICC given by the GSMA.
Key benefits of the iSIM
The main benefit of the iSIM is that it helps to radically simplify device design and manufacture, while reducing the management burden by limiting the number of vendors and service providers required to operate a device. The iSIM not only provides a streamlined experience for customers, mobile operators and OEMs, but allows all parties to reap the benefits, including:
- Simplifying connectivity
The iSIM is fully compatible with 2G, 3G, 4G and 5G networks, and can be used in any cellular consumer device. It can also be deployed in consumer IoT and M2M devices, allowing connected devices to operate from anywhere. The iSIM is also compliant with the GSMA Remote SIM Provisioning Consumer & M2M and ETSI SIM specifications. This means one can rely on the existing eSIM infrastructure to manage the iSIM.
- Reducing costs & energy consumption
While an eSIM relies on a separate chip, the iSIM is hosted on a single SoC along with a cellular modem and microcontroller unit. With fewer steps and materials needed to assemble the iSIM, costs for manufacturers are lowered across the supply chain. Energy consumption is also reduced thanks to the advanced technology node employed to build the SoC.
- Same security certification
The iSIM is fully standardised and endorsed by the industry and is recognised by several industry bodies including the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI), Eurosmart, Trusted Connectivity Alliance and the GSMA. The assurance requirements that apply to the iSIM ensure the same security certification level as the eSIM is achieved.
However, in order to provide secure access to the cellular network, the iSIM must be personalised with remote management credentials during the manufacturing process. So how can this be achieved without affecting device manufacturers?
Introducing 2-step personalisation
While the iSIM is a new means to authenticate devices on mobile networks, this should guarantee the security level remains unchanged. Data security needs to be ensured not only when managed by the secure area chip, but also while it is processed at the manufacturing of devices. This requires implementing specific security measures in factories and having them certified.
Two-step personalisation is a new way to secure provision credentials in a tamper-resistant element that allows consumer electronics and IoT OEMs to fulfill these needs without incurring the burden of security management.
Two-step personalisation securely splits personalisation steps between the SoC manufacturer and the iSIM provider such as Thales. Both players establish together a trusted relationship that enable them to prepare separately the SoC and the iSIM using GSMA approved processes named Perso SC and Perso UICC respectively. This allows the device manufacturer to use the SoC as usual as the iSIM is seamlessly deployed with the required credentials when the SoC firmware is loaded onto the device. The iSIM provider then securely activates the iSIM to turn into a fully functional eSIM.
Thanks to 2-step personalisation, the device manufacturer flow remains unchanged and does not require extra certification, while adhering to the GSMA production security standards. This lowers dramatically the impact on OEM manufacturing sites and streamlined processes, reducing the effort to deploy cellular connectivity in devices while keeping the process secure.
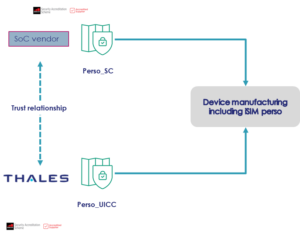
Thales is the first company in the world to introduce 2-step personalisation, and has recently been granted the world’s first 2-step personalisation GSMA SAS-UP certification for its data centre in Tours, France.
Now 2-step personalisation can be implemented in an industrial and secure manner. This marks a significant shift towards the large-scale commercial deployment of integrated SIM technologies.
Interested and want to learn more about the iSIM and its role in enabling the secure connectivity of devices? Leave a comment below and make sure to follow us on Twitter at @ThalesDigiSec!
For further info:



