5G connectivity is set to power a whole new host of services. By 2025, it will account for 21% of the world’s mobile connections. It also has the power to unlock the potential of the Internet of Things (IoT) by unleashing a combination of speed, low latency, expanded bandwidth and increased power efficiency for connecting objects In this blog series, we will explore the different verticals and industries that are set to be powered and revolutionized by 5G technology – starting with smart manufacturing.
Industrial Revolution to Industry 4.0
In 1712 the first steam engine was invented. This milestone is often cited by historians as the beginning of what became known as the industrial revolution; a revolution that is so named because it fundamentally transformed economies, lives, and societies beyond previous recognition.
Another key milestone of this revolution took place 150 years ago with the inception of the production line; turning the manufacturing sector on its’ head. Mass production and assembly lines drastically improved the speed – and decreased the cost – of making everyday items.
Jump forward to present day, and the sector is subject to another game-changer – 5G. Thanks to 5G, the manufacturing sector is entering the era of IoT-enabled smart production, also known as Industry 4.0 or the industrial IoT.
When McKinsey evaluated the economic impact in 2030 across a range of business areas, the factory area had the greatest economic potential. The researchers estimated that the impact of IoT in factories could range from US$1.4 trillion to US$3.3 trillion by 2030. In fact, factories could represent 26% of IoT’s complete economic potential in 2030. Manufacturing itself will grow from US$1 trillion to US$2.3 trillion.
The research suggests that the greatest possible gain, and to create value, lies in optimizing manufacturing operations and improving management of assets and people.
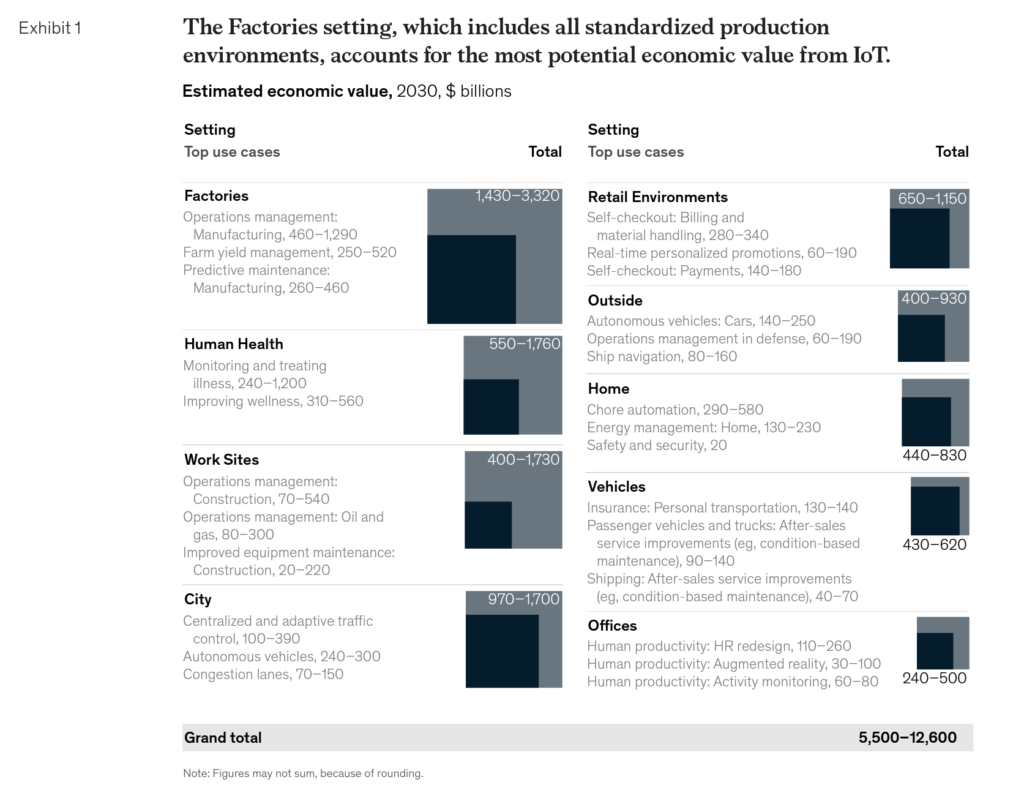
Figure: Factories lead in estimated economic value in 2030
Source: McKinsey
How 5G Powers the Industrial IoT Era of Manufacturing
We’re now entering the era of smart machines, or ‘smart manufacturing’. Smart manufacturing allows factory managers to automatically collect and analyse data to make better-informed decisions and optimize production.
It’s been said that 5G is the first network that was built to serve the needs of the industrial sector, for the following reasons:
High bandwidth, speed and low latency
5G can support up to a thousand times more bandwidth than a 4G network, and tops out at 10 gigabits per second – meaning it can be relied upon for the exchange of vast amounts of data in real-time.
Now, with the latest 5G Release 16 we have started on the road to ultra-reliable low latency communication (URLLC) which will be super-critical for smart manufacturing.
Connectivity
For manufacturing to be truly ‘smart’, ease of connectivity between IoT enabled devices is required. 5G allows for this by offering ten times the level of connectivity compared to 4G.
Energy efficiency
5G networks on average use 90% less energy per bit of data in comparison to 4G; a game-changer in the current climate with the rising cost of energy.
Keeping mission critical operations private
5G Private Networks represent powerful tools for mission and business-critical enterprises to improve the efficiency and safety of their operations. Private Networks must offer a seamless and secure experience from the initial connection and throughout day-to-day usage.
The network slicing element of 5G is compelling. Now is the time when public networks are starting to deploy Release 16. This provides improved security and control because you are either on a public network with a manufacturing slice and guaranteed SLAs for diverse services, or you’re on a private network with your parameters set by you so you can have improved quality of service
Manufacturing itself is going through digital transformation and a comprehensive approach is needed to solve challenges relating to device security, 5G introduction, quality control and device deployment.
The impact of 5G on Manufacturing
So, that covers the benefits of 5G – but how will it impact manufacturing outcomes specifically? Just some of the examples include:
Keeping track of products and assets
The use of smart sensors will give factory managers the insights they need to track production with real-time view of output. This same level of visibility can be extended across the entire supply chain, giving them potential access to real-time data from their transport and logistics partners.
Reduction of waste
According to the World Economic Forum, industrial waste makes up at least 50% of waste generated globally, with manufacturing one of the biggest contributors. The proper use of data and automation has been mooted as a solution to combat this by using data to make complex, high volume solutions that minimize wastage.
Improve energy efficiency
Whether it’s turning off idle machines that aren’t needed or making decisions about what should be produced and when based on energy consumption – IoT can help factories become more energy efficient.
Monitor product quality
The addition of environmental sensors inside factories could help companies improve the quality of their goods. The sensors can send alerts when conditions drop below ‘optimal’.
Predictive maintenance
IoT can help identify faults before they even happen. Sensor data can help detect when a machine is showing signs of malfunction before it ceases to work completely, saving time and costs.
Want to know more?
- Explore smart manufacturing further on the Thales website
- Watch our video: ‘What is Smart Manufacturing’



