Business organisations today are handling massive volumes of data at various levels in their operation. With digitization being implemented on a huge scale, data breach is now among the primary concerns that business entities are either facing or fearing. A recent study found that 60% of the businesses surveyed revealed that their data had been breached at some point of time, of which 30% of the respondents stated that they had been victims of data breach in the past year itself.
In this blog post, we will touch upon data masking – one of the most popular ways to secure sensitive data.
What Is Data Masking?
While most organizations have stringent cybersecurity measures in place for protecting data in production and storage phases, the situation tends to become more complex in the data use process. The chances of data breaches intensify when the data of an organization ends up being utilised for operations that can hardly be termed as adequately secure. The scenario is further compounded when these operations are outsourced by the organization to an external agency because that translates to the organization having lesser control over the environment in which the data is used. This coupled with the reality that governments across the globe are enacting stricter data protection compliances (EU’s GDPR and India’s upcoming Data Protection Bill, to name a few), only enhances the urgent need for acquiring professional data protection.
Data masking, also known as data obfuscation, operates by shielding confidential data, such as credit card information, social security numbers, names, addresses, contact information, etc. from unintended exposure to reduce the risk of data breaches. It protects data in cases where the data may become visible to someone who does not have clearance to view the said data. For instance, let us assume that your organization has engaged a contractor to build a database. With data masking, the contractor can evaluate the database without actually accessing sensitive information like client details.
In data masking, the format of data remains the same – only the values are changed. The data may be altered in a number of ways, including encryption, character shuffling, and character or word substitution. Whatever method is chosen, the values must be changed in a way that makes detection or reverse engineering impossible. The key to data masking is keeping the data formats unchanged while changing the data values so that the actual data is obfuscated.
What Types Of Data Can Be Protected With Data Masking?
While the types of data that can be protected through data masking are several, following are the kinds of data that are most commonly protected through data masking by organizations:
1. PII (Personally Identifiable Information)
2. PHI (Protected Health Information)
3. PCI-DSS (Payment Card Information)
4. Intellectual Property
What Are The Types Of Data Masking?
Data masking can be broadly classified into the following two categories:
1. Static Data Masking – Static data masking permanently replaces sensitive data by altering data at rest.
2. Dynamic Data Masking – Dynamic data masking aims to replace sensitive data in transit while leaving the original at-rest data intact and unaltered.
What Are The Techniques Used For Data Masking?
Following are a few techniques that can be incorporated in the data masking process:
1. Encryption: When data is encrypted, only authorized users can access it using a digital key.
2. Character Scrambling: This is when characters in the original data are jumbled so as to render the data unidentifiable.
3. Nulling Out or Deletion: This method ensures that the data becomes null and void for those who are not authorized to access it.
4. Substitution: Here, the actual value of the real data is mimicked by the substitute value that is assigned to the said data to ensure its protection.
5. Tokenization: It is a method in which the sensitive data stored in relational databases and files is replaced with non-sensitive placeholder tokens.
What Is The Ideal Strategy For Implementing Data Masking?
If the following four steps are followed, data masking endeavors will yield the best results:
1. Find data such that sensitive data is identified and distinguished.
2. Assess the sensitive data in all aspects including location of storage, the data masking technique that is most suited to the data at hand, etc.
3. Implement data masking such that at times, a combination of data masking techniques may have to be employed.
4. Test the results of the data masking technique(s) administered to understand if the whole process is going in the right direction or not.
What Are The Applications Or Use Cases Of Data Masking?
The Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI) has launched a feature called ‘Masked Aadhaar’. It is quite similar to regular Aadhaar (which is a unique identification number assigned to Indian citizens that differs from citizen to citizen) but the difference is that the Aadhaar number is partially covered. The Masked Aadhaar feature allows users to partially hide their 12-digit unique identity in their downloadable e-Aadhaar copy. Only the last four digits are visible, while the remaining are hidden.
On a global note, PCIDSS introduced guidelines to make data masking of credit card information mandatory with the aim of strengthening data security regarding usage of credit card information by third party business units and/or at the backend of various corporate entities.
Recommended audit and compliance practices from all over the world suggest that third party vendors have to facilitate data masking of confidential data that is identified by the concerned business or by the risk and compliance departments of the respective organizations or banks. This is particularly important in light of the recent controversy involving a large bank in India, which faced challenges with respect to security of confidential customer data that was shared within the bank as well as with third party vendors. However, the bank stated that the incident was a case of misreporting and affirmed, “The incident under question is related to a service in which account data is quickly made available to a customer through an outgoing SMS service after taking care to mask account details so that customer data is protected. The masking in any case ensures that there is basic protection for the customer data.”
What Are The Advantages Of Data Masking?
1. Data masking effectively provides a solution to five key issues surrounding data – data breach, data loss, data hijacking, insecure data interface, and unauthorized data use by insiders in an organization.
2. It allows the integrity and structural format of the original data to be retained.
3. It enables sharing of data with authorized persons without there being chances of the production data being revealed.
4. It reduces risks involved in data usage in a cloud environment.
5. It is comparatively pocket-friendly and uncomplicated.
To Sum It Up
With an increasing focus on protecting the privacy and confidentiality of users’ data, and chances of the Personal Data Protection Bill being enacted in the upcoming winter session in India being brighter than ever before, technologies around data masking will be widely adopted across all verticals to safeguard sensitive data.
How Gemalto Can Help
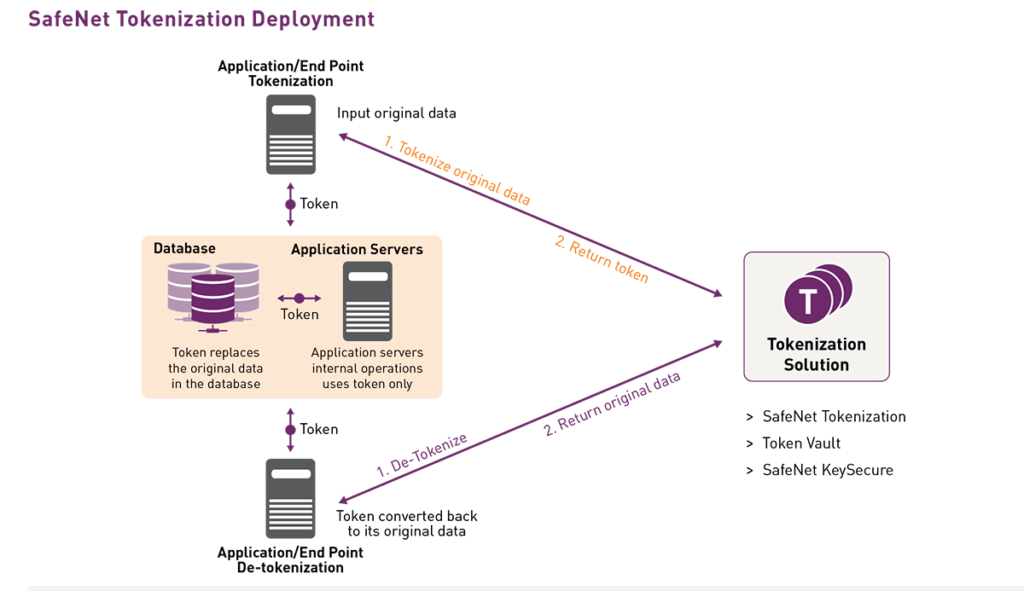
Gemalto – A Thales company, is a trusted provider of data masking services. As a global leader of data protection services, Gemalto offers end-to-end data masking and tokenization services with its SafeNet Tokenization that can be leveraged to fit the unique needs of a business.
Know more about how Gemalto can help mask your data and see below is a quick pictorial overview of Gemalto’s SafeNet Tokenization: